Understanding Redis: A Comprehensive Guide to Key Data Types and Commands
Quick overview of Redis data types because most time people is confuse
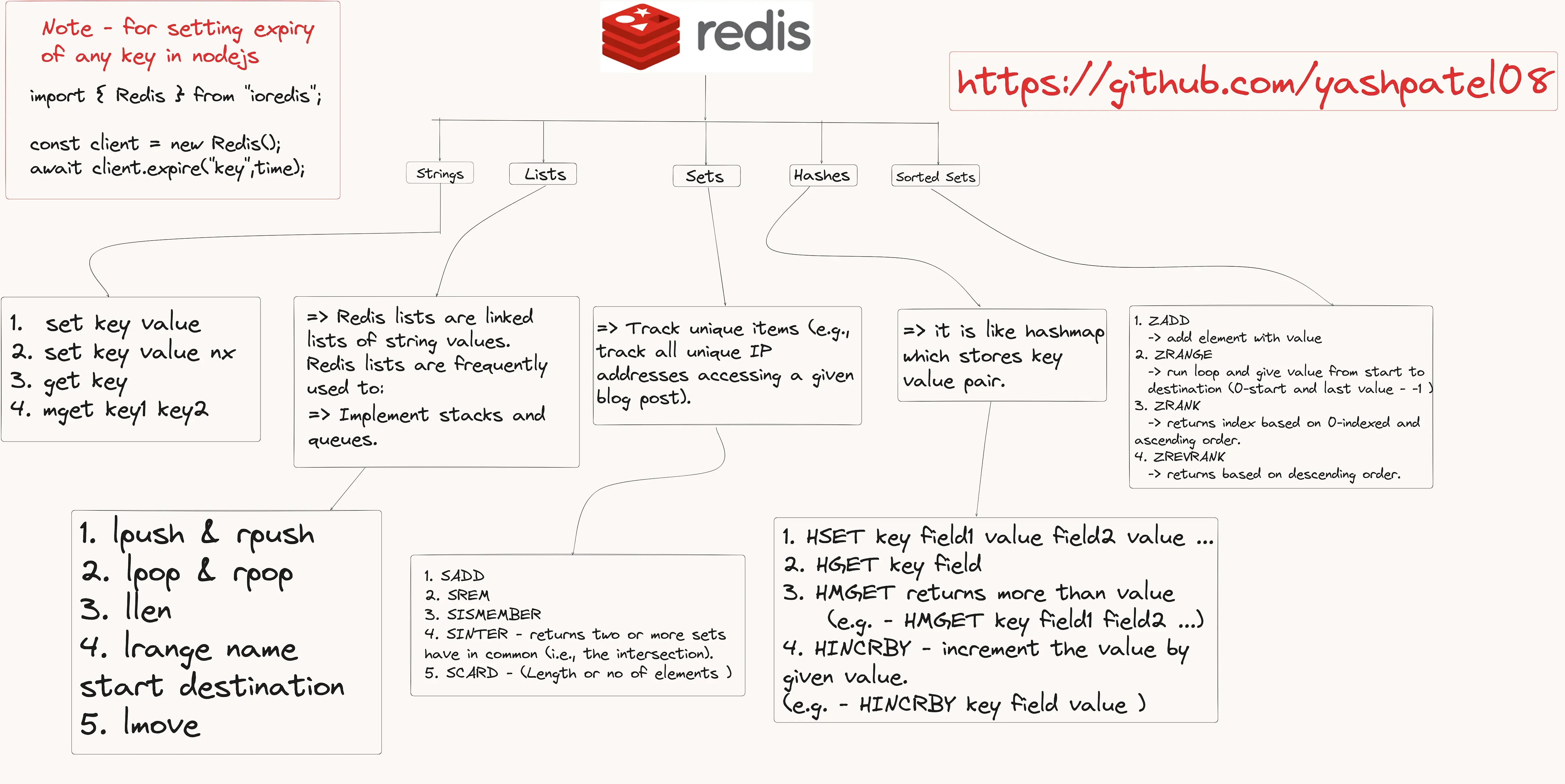
Redis is a powerful in-memory data store that can function as a database, cache, and message broker. Its versatile data structures and commands make it an essential tool for developers looking to build high-performance applications. In this blog, we will delve into the core data types and commands in Redis, with a focus on practical use cases and code examples using ioredis for Node.js.
- Strings
Strings are the simplest data type in Redis. They are binary-safe and can hold any data, such as text or serialized JSON.
- SET: Stores a string value.
- SET: Stores a string value.
1await client.set('key', 'value');
- SETNX: Stores a string value only if the key doesn’t already exist, useful for implementing locks.
1await client.setnx('key', 'value');
- GET: Retrieves a string value.
1const value = await client.get('key');
- MGET: Retrieves multiple string values in a single operation.
1const values = await client.mget('key1', 'key2');
- Lists
Redis lists are linked lists of string values. They are frequently used to implement stacks and queues.
- LPUSH: Adds a new element to the head of a list.
1await client.lpush('list', 'value');
- RPUSH: Adds a new element to the tail of a list.
1await client.rpush('list', 'value');
- LPOP: Removes and returns an element from the head of a list.
1const value = await client.lpop('list');
- RPOP: Removes and returns an element from the tail of a list.
1const value = await client.rpop('list');
- LLEN: Returns the length of a list.
1const length = await client.llen('list');
- LRANGE: Extracts a range of elements from a list.
1const elements = await client.lrange('list', 0, -1);
- LMOVE: Atomically moves elements from one list to another.
1await client.lmove('source', 'destination', 'LEFT', 'RIGHT');
- Sets
Sets are unordered collections of unique strings. They are useful for tracking unique items, such as unique IP addresses accessing a blog post.
- SADD: Adds a member to a set.
1await client.sadd('set', 'member');
- SREM: Removes a member from a set.
1await client.srem('set', 'member');
- SISMEMBER: Checks if a value is a member of a set.
1const isMember = await client.sismember('set', 'member');
- SINTER: Returns the intersection of multiple sets.
1const intersection = await client.sinter('set1', 'set2');
- SCARD: Returns the number of elements in a set.
1const count = await client.scard('set');
- Hashes
Hashes are maps between string fields and string values, making them ideal for representing objects.
- HSET: Sets the value of a field in a hash.
1await client.hset('hash', 'field1', 'value1');
- HGET: Gets the value of a field in a hash.
1const value = await client.hget('hash', 'field1');
- HMGET: Gets the values of multiple fields in a hash.
1const values = await client.hmget('hash', 'field1', 'field2');
- HINCRBY: Increments the value of a field in a hash by a given number.
1await client.hincrby('hash', 'field', 1);
- Sorted Sets
Sorted sets are similar to sets but where every member is associated with a score. They are used to implement leaderboards.
- ZADD: Adds a member to a sorted set, or updates its score if it already exists.
1await client.zadd('zset', 1, 'member');
- ZRANGE: Returns a range of members in a sorted set, by index.
1const members = await client.zrange('zset', 0, -1);
- ZRANK: Returns the rank of a member in a sorted set, with the scores ordered from low to high.
1const rank = await client.zrank('zset', 'member');
- ZREVRANK: Returns the rank of a member in a sorted set, with the scores ordered from high to low.
1const rank = await client.zrevrank('zset', 'member');
Expiry
To set the expiry of any key in Node.js using ioredis:
1import { Redis } from 'ioredis';23const client = new Redis();4await client.expire('key', time);
Conclusion
Redis is a versatile and powerful tool for any developer’s arsenal. Its various data types and commands allow for efficient data storage and retrieval, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Whether you’re implementing a simple cache, a message broker, or a complex data store, Redis has the tools you need. Happy coding!
#Redis #NodeJS #ioredis #TechLearning